HRNet Series
Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Visual Recognition
Lite-HRNet: A Lightweight High-Resolution Network
HRFormer: High-Resolution Transformer for Dense Prediction
Table of contents
Summary
일반적으로 deep learning에서는 high dimension data가 low dimension manifold에서 분포할 수 있다고 가정한다. 이미지같은 고차원 데이터도 network layer를 통하며, 효과적으로 압축하고, 그 내재된 구조를 학습하여 좋은 일반화 성능을 보일 수 있다. 하지만, Classification과 같은 task와 다르게, Pose Estimation, Semantic Segmantation과 같은 dense prediction은 pixel 단위의 정밀한 prediction이 필요하기 때문에, high-resolution의 feature 유지가 중요하게 생각된다.
High-resolution의 feature를 유지하기 위해, skip connection이나 upsampling과 같은 방법들이 많이 사용되지만 low-resolution에서는 high-resolution의 feature representation을 학습하기 힘들다.
따라서, HRNet은 여러 해상도의 parallel stream을 구성하고, 각 stream의 feature map을 fusion 하여, low-resolution부터 high-resolution의 feature를 연결한다. 이로인해, 각 feature map이 high-resolution의 representation을 유지하면서, low-resolution의 general feature를 효과적으로 학습할 수 있게 설계한다.
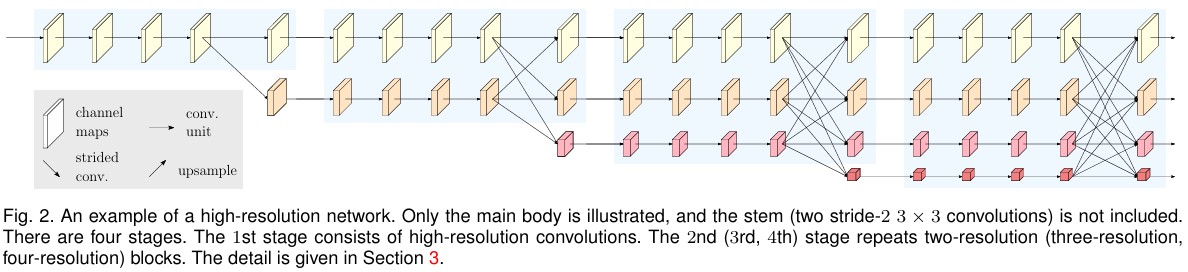
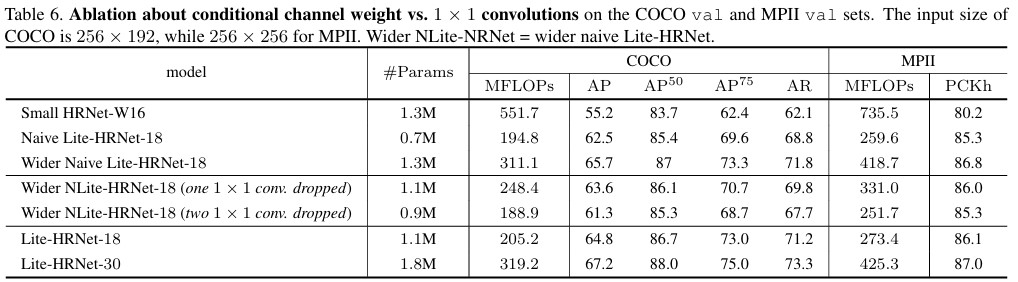
HRNet과 같이 고해상도 특징을 지속적으로 유지하는 네트워크들은 pose estimation, object detection, semantic segmentation 등에서 좋은 성능을 보이지만, mobile 및 embedded와 같은 제한된 resource에서는 활용하기 힘들다. 따라서, Lite-HRNet에서는 HRNet을 경량화하여 효율적으로 inference 할 수 있는 model을 설계했다.
일반적으로, 여러 resolution의 feature map을 섞기 위해, 1x1 convolution이 많이 사용된다. 하지만, 이는 channel에 대해 선형적인 시간 복잡도를 가지기 때문에, Lite-HRNet에서는 ShuffleNet의 Shuffle block과 Conditional Channel Weighting을 통해 경량화를 수행한다.
HRFormer는 Vision Transformer가 여러 Vision Task에서 뛰어난 성능을 보인 것을 참고하여, HRNet에 Transformer를 활용하였다. CNN으로 구성된 HRNet의 Body 부분을 Transformer로 대체하였다. Transformer의 경우 일반적으로, input이 patch로 나뉘어 Attention 및 FFN layer에 들어간다. 즉, token 별로 sequence를 처리하기 때문에 각 token별 representation 학습이 쉽지 않다. 따라서, swin이나 window, shuffle과 같은 방법들이 쓰이고, HRFormer에서는 FFN layer에서 depth-wise convolution을 적용하여 여러 feature representation을 연결한다.
HRNet
HRNet의 stem은 2개의 2 stride 3x3 Convolution으로 이뤄져 있다. Stem은 input을 $\frac{1}{4}$ resolution으로 줄어든 후, main body의 입력으로 사용된다.
Body는
- 여러 resolution 의 parallel stream으로 분리되는 부분
- 각 resolution stream을 fusion하는 부분
- Task에 따라 output을 출력하는 head 부분
으로 나뉜다.
Parallel Multi-Resolution Convolutions
High-resolution stream에서부터 low-resolution stream을 점진적으로 추가하여, parallel stream을 구성하는 부분이다. 아래와 같은 방식으로 parallel stream이 구성되며, \(\mathcal{N}_{sr}\)에서 \(s\)는 netwokr layer의 depth를 의미하고, \(r\)이 stream index를 의미할 때, resolution은 첫 stream 대비 \(\frac{1}{2^{r-1}}\)의 resolution을 가진다.
Repeated Multi-Resolution Fusions
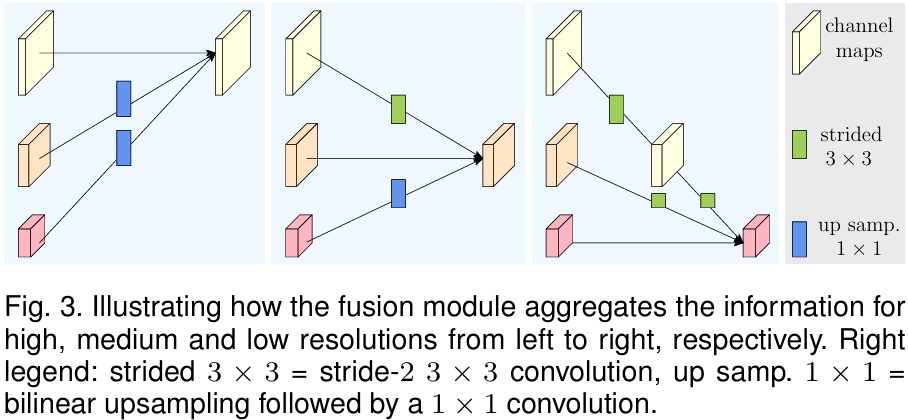
각 resolution stream의 representation을 학습하기 위해 fusion module이 사용된다. 논문에서는 4개의 residual unit마다 fusion을 수행해준다. Fusion은 각 stream에 aggregation되는데, channel 수와 resolution을 target stream에 맞게 변형한 후 feature map을 더하여 수행된다.
Resolution에 따라,
- Upsampling: Bilinear upsampling 후, 1x1 convolution
- Downsampling: stride 2의 3x3 convolution 을 통해 수행된다.
그림으로 나타난 과정을 하기 그림과 같다.
Representation Head
HRNet은 task 및 목적에 따라 3개의 head를 제안한다.
- HRNetV1: High-resolution stream에서만 representation을 출력
- HRNetV2: 각 stream의 feature map을 High-resolution stream에 aggregation 하여 representation을 출력
- HRNetV2p: HRNetV2의 output을 여러 level로 downsampling하여 representation을 출력
논문에서는 HRNetV1을 Pose Estimation, HRNetV2를 semantic segmentation, HRNetV2p를 object detection에 적용하였다.
Architecture & Human Pose Estimation
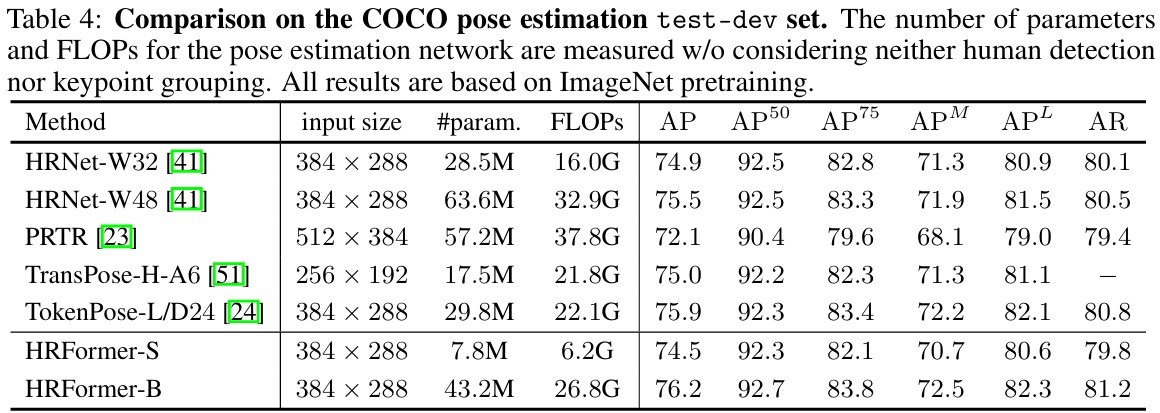
HRNet은 stem에서 \(\frac{1}{4}\) resolution으로 representation을 출력하기 때문에 main body에서 각 stream의 resolution은 \(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{1}{8}, \frac{1}{16}, \frac{1}{32}\)로 구성된다. 각 stream의 convolution channel은 \(C, 2C, 4C, 8C\)로 구성되어 있다. 자세한 architecture는 하기 표와 같다.
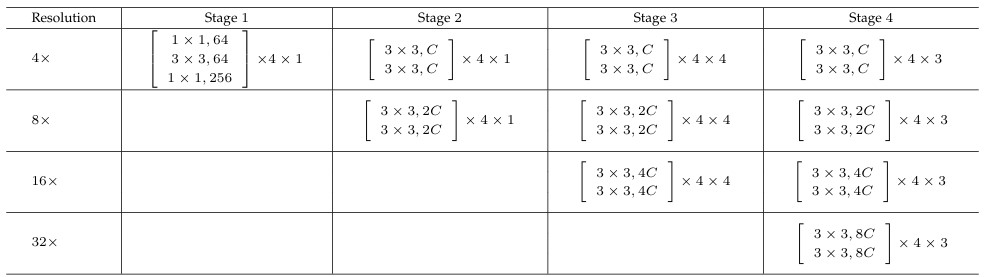
HENet은 각 해상도에서 representation을 학습하는 반면, fusion 단계에서 representation을 섞어주기 때문에 group convolution과 같이 다양한 feature를 학습하는 효과를 얻을 수 있다. HRNet은 여러 resolution에서 representation을 학습하고 fusion을 통해 representation을 학습하는데 뛰어난 효과를 보인다.
HRNet의 human pose estimation은 K개의 keypoint에 대해 heatmap을 추정한다. Heatmap은 이미지의 각 위치에서 해당 관절이 존재할 확률이나 신뢰도를 나타내는 2차원 맵(heatmap)을 생성하는 것을 의미한다.
일반적으로 실제 관절 위치 주변에는 2D Gaussian 분포와 비슷한 형태의 높은 값이 나타나고, 그 외의 부분은 낮은 값이 나오도록 학습시킨다. 직접 좌표를 regression하는 것보다 heatmap 방식은 spatial representation을 보존하면서 더 안정적으로 학습할 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
\(H_k\)가 \(k\)th keypoint의 heatmap을 의미할 때,
로 나타나고, MSE Loss는
\[\begin{gather} \mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{K}\sum^k_{k=1}\sum_{x,y}(\hat{H}_k(x,y)-H_k(x,y))^2 \end{gather}\]와 같이 계산된다.
추가적으로, HRNet은 bbox prediction은 SimpleBaseline을 활용하고, 평가 metric으로는 OKS(Object Keypoint Similarity)를 사용한다.
\[\begin{gather} OKS: \frac{\sum_i\exp{(-d_i^2 / 2s^2k^2_i)}\delta(v_i > 0)}{\sum_i \delta(v_i > 0)} \end{gather}\]추가적인 자세한 내용은 논문의 section 4 참조
Lite-HRNet
Lite-HRNet은 HRNet과 같이 high-resolution representation을 유지하며 mobile, embedded 환경에서 dense prediction에서 높은 성능을 내기 위해 설계된 light-weight model이다.
ShuffleNet의 shuffle block과 CCW (Conditional Channel Weighting) Unit의 적용이 주 내용이자 contribution으로 볼 수 있다.
Naive Lite-HRNet
ShuffleNet V2는 1x1 Convolution의 계산량을 줄이기 위해, channel split 후, 한 branch에 DWS Convolution을 적용하고, 나눠졌던 두 channel을 concatenate하도록 설계했다.
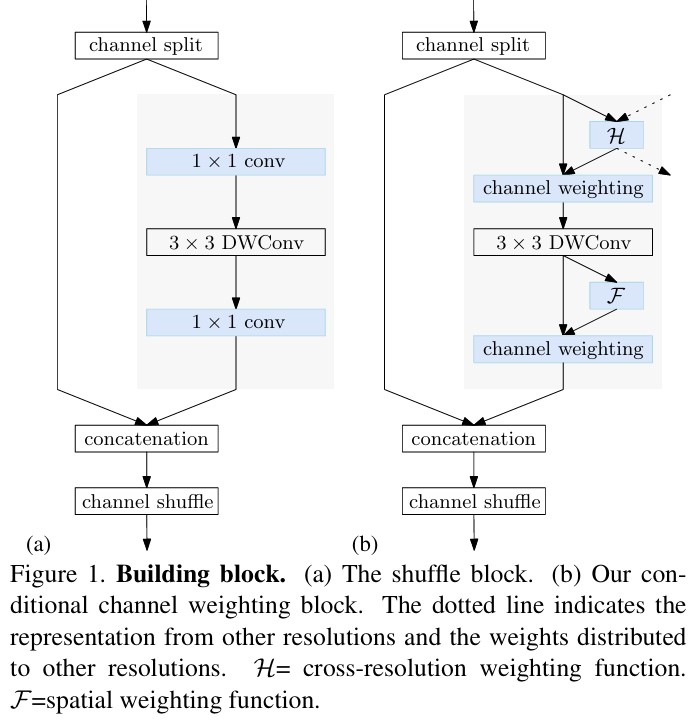
Lite-HRNet은 전체적으로 Small HRNet 구조에서 조금 더 경량화한 구조를 따른다.
- Stem의 두번 째 Convolution과 모든 residual block을 Shuffle Block으로 교체
- multi-resolution fusion은 separable convolution으로 대체
Lite-HRNet
Conditional channel weighting
1x1 convolution의 경우 \(C_{in}, C_{out}\)에 대해 계산을 진행해야하기 때문에, \(mathcal{O}(C^2)\)의 복잡도를 가진다.
반면, depthwise convolution은 3x3일 때, \(mathcal{O}(9C)\)의 복잡도를 가지기 때문에 상대적으로 light하다. 따라서 1x1 convolution을 Conditional channel weighting으로 대체하여 계산량을 줄인다.
Conditional channel weighting은 \(s\)-stage에서 다음과 같이 계산된다. (\(s\)-stage에는 \(s\)개의 resolution이 존재)
Element-wise로 계산이 진행되고, \(W_s \in \mathcal{R}^{W_s \times H_s \times C_s}\)일 때, \(X_s \in \mathcal{R}^{C_s}\)로 복잡도가 \(mathcal{O}(C)\)로 1x1 convolution보다 가볍다.
Figure 8.b와 같이, channel weights는 단일 resolution이 아닌, 여러 resolution으로부터 결정된다.
Cross-resolution weight computation
Figure 4.b와 같이, channel-wise의 conditonal weighting \(\mathcal{H}\)는 \(X_1\)이 가장 큰 resolution일 때,
\[\begin{gather} (W_1, W_2, \ddots, W_s) = \mathcal{H}(X_1, X_2, \cdots, X_s) \end{gather}\]으로 나타내진다.
\(\mathcal{H}_s(\cdot)\)은 가장 작은 resolution \(X_s \in \mathcal{R}^{W_s \times H_x}\)로 AAP(Adaptive Average Pooling)을 수행하여 모든 resolution을 concatenate한다.
\[\begin{gather} X_i'=AAP(X_i) \end{gather}\]이후, 1x1 convolution, RELU, 1x1 convolution, sigmoid를 통해 weight \(W_i'\)를 도출하고, 각 resolution에 대해 Upsampling을 하여 최종 weight \(W_i\)를 얻는다.
Input \(X_i'\)와 \(W_i'\)의 channel수가 같기 때문에 channel들이 각 input resolution에 mathching되고, upsampling을 하기 때문에 element-wise로 conditional channel weighting이 계산된다.
최종적으로 \(s\)-stage에 대해 Cross-resolution weight computation은 아래와 같다.
\[\begin{gather} X_i'=AAP(X_i), \quad \text{where} \quad i=1,\cdots,s \\ X_{in}'=\text{Concat}(X_i, \cdot X_s) \\ X_h = \text{RELU}(\text{1}\times\text{1Conv}(X_{in})) \\ W_{out}'= \text{Sig}(\text{1}\times\text{1Conv}(X_h)) \\ W_{out} = \text{UpSampling}(W_{out}') \\ W_i = \text{Split}(W_{out}) \quad \text{where} \quad i=1,\cdots,s \end{gather}\]이를 통해, 각 resolution은 다른 resolution의 정보를 받아, weighting을 수행하며, 일반적인 1x1 convolution의 역할을 대체한다. 또한, 가장 작은 resolution의 spatial에 따라, 계산이 되기 때문에 하기 표와 같이 계산 복잡도에서도 이점이 있다.
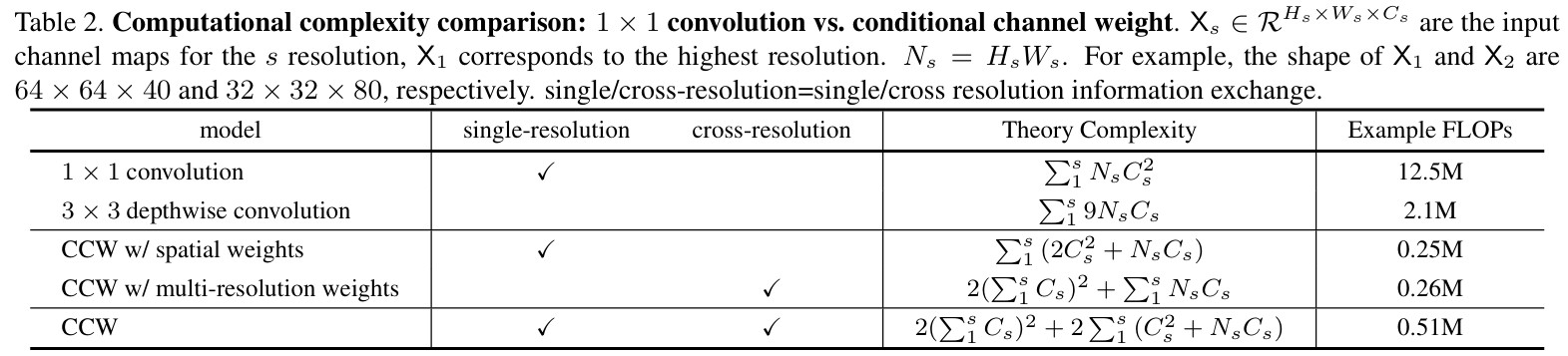
Spatial weight computation
Figure 8.b에서 \(\mathcal{F}\)는 GAP, FC, ReLU, FC, Sigmoid를 통해 수행된다. 같은 channel에서는 spatial position에 상관없이 같은 weight를 가지고 이는 전체 resolution의 spaital information을 합쳐 weighting하는데 도움을 준다.
Architecture & Human Pose Estimation
Lite-HRNet은 HRNet과 비슷하게, High-resolution을 stride 2 convolution과 shuffle block을 통해 줄이는 stem으로 시작한다.
Main body는 2개의 CCW block과 1개의 Fusion block으로 이뤄진다.
\(\rightarrow\) Fusion block은 depth-wise separable convolution
Stage에서 각 resolution의 channel은 main의 input channel이 C일 때, C, 2C, 4C, 8C의 형태를 가진다.
EfficientNet 등은 sub-network를 통해 작은 parameter로도 model capacity를 높이지만, Lite-HRNet에서는 여러 stage의 weighting을 통해 1\(\times\)1 Convolution과 비슷한 효과를 내면서 lightweight network를 달성한다.
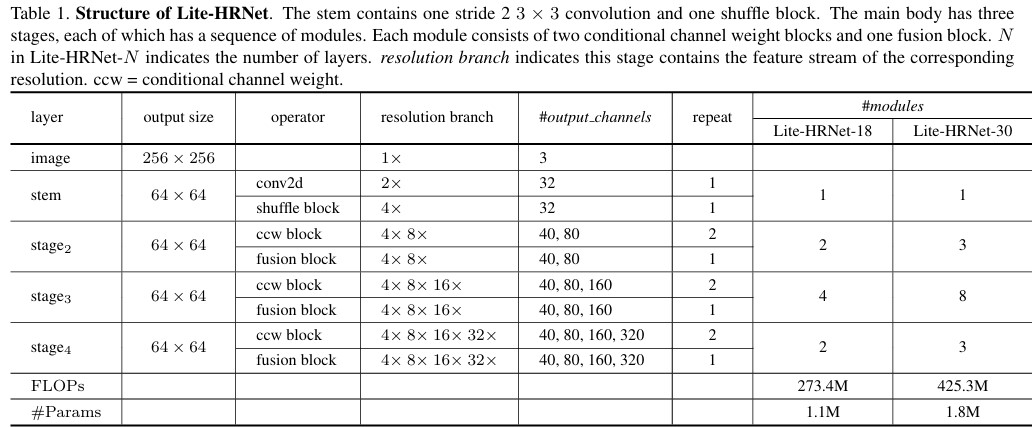
Lite-HRNet은 8개의 V100 GPU에서 32 batch로 adam, 2e-3 lr로 훈련했으며, 결과는 하기 표와 같다.
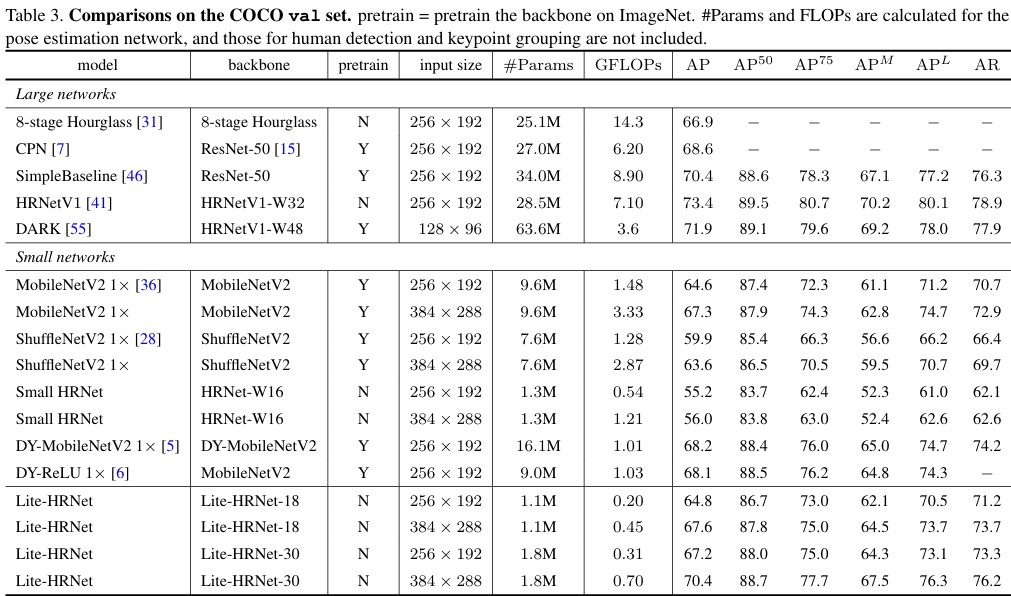
HRFormer
ViT(Vision Transformer)는 Classification 등의 task에서 좋은 성능을 보였고, BeiT, DeiT, Swin Transformer와 와 같은 모델들은 distillation, data augmentation, window & shifting 등을 통해 그 성능을 높였다.
ViT는 입력 이미지를 일정 크기의 패치로 나눈 뒤 embedding을 통해 token sequence로 변환한다. 하지만 이런 작업은 세밀한 position information을 잃기 쉽고, 고정된 path size를 사용하기 때문에 multi-scale에 대한 modeling이 쉽지 않다. 또한 계산량이 많아서 dense prediction과 같은 작업에 부정적인 영향을 미친다.
HRFormer는 HRNet의 architecture를 차용하여 high resolution의 feature representation을 유지하며 dense prediction에서도 transformer를 통해 높은 성능을 얻는 것을 목표로 한다.
HRNet의 구조를 사용하며 Local-window self-attention을 통해 계산량을 줄이고, FFN 내에 depth-wise convolution을 도입하여 local window간의 representation 학습을 효과적으로 수행할 수 있게 한다.
High-Resolution Transformer
Multi-resolution parallel transformer
HRNet과 같이, stem 이후 main body에서 high resolution부터 시작하여, stage 마다 low resolution을 가지는 parallel stream을 추가해나가는 방식으로 구성된다. 각 stream은 transformer block을 통해, representation을 학습하고 convolutional multi-scale fusion을 통해 stream 간 representation을 교환한다. convolutional multi-scale fusion은 HRNet과 동일하고, transformer block에서 차이점이 존재한다.
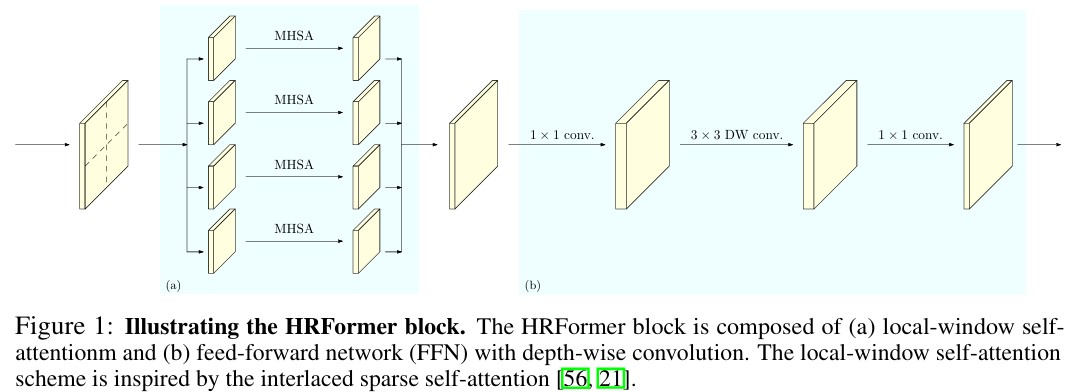
Local-window self-attention
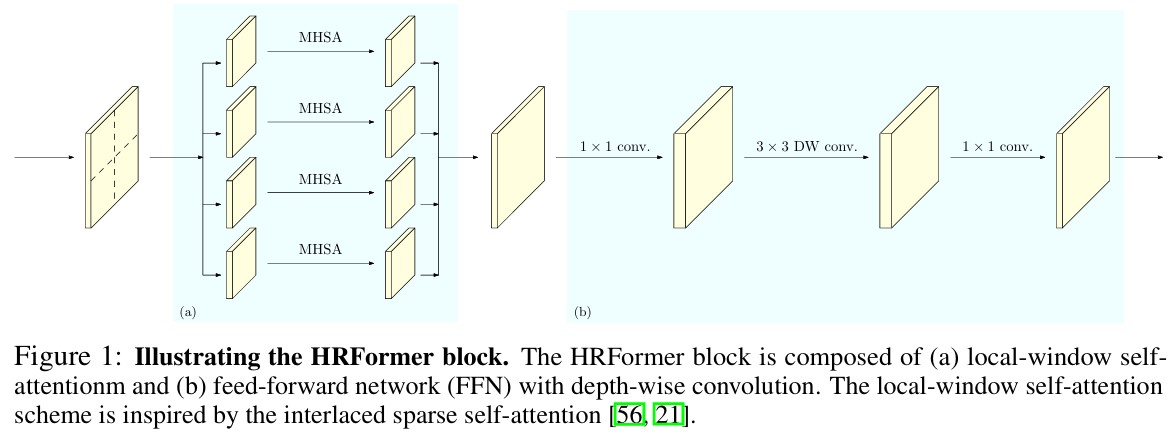
Transformer block에서 feature map은 overlap되지 않은 \(K \times K\) window로 나뉜다. 각 window에서 독립적으로 MHSA가 수행된 후, 각 window의 output을 merge하여 output을 계산한다.
MHSA와 merge의 수식 및 과정은 아래와 같다.
추가적으로, local-window self-attention에 T5의 relative position information을 적용헸다.
T5의 relative position information
Relative position information은 Query와 Key의 상대적 거리를 통해 공간 위치 정보를 학습하는 방식
Self-attention은 기본적으로 matrix 연산이기 때문에 order-independent고 transformer에 명확한 positional information을 제공할 수 없음
따라서, sinusoidal 등을 통해 positional embedding을 token에 더하여 위치 정보를 주는데 relative position information은 고정된 position을 사용하지 않고, token간 상대적인 위치 차이에 따라 다른 학습된 embedding을 사용
Relative position의 경우 가능한 거리가 일반 position에 비해 2배가 길기 때문에 bucket 방식을 통해 parameter 수와 model stabilize를 높임Non-uniform Quantization과 비슷하게 가까운 거리에는 많은 parameter를 할당
먼 거리(상대적으로 덜 중요하다고 판단)는 묶어서 같은 값을 할당하여 하나의 bucket으로 취급
모델이 어떤 상대적 위치가 어텐션 계산에 얼마나 큰 영향을 미쳐야 하는지를 스스로 학습또한, 각 bucket에 trainable parameter를 할당하여 훈련 과정에서 attention에 대한 weight를 학습
이 parameter는 효율성을 위해, 모든 layer가 공유하지만, layer내의 각 head는 다른 값을 사용
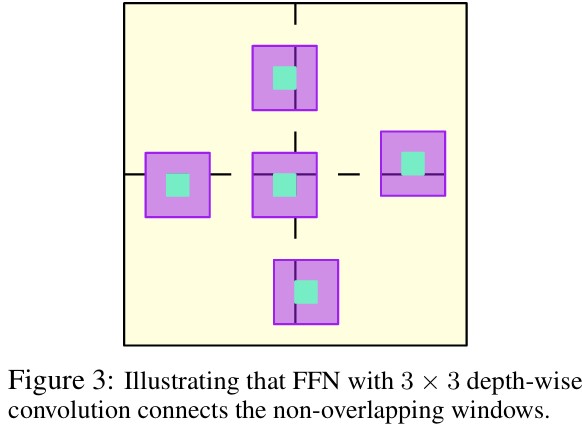
FFN with depth-wise convolution
Local-windowself-attention은 overlap없이 windowing되기 때문에 각 window간 정보 교환이 없다. 따라서, FFN 단에서 두 MLP 사이에 \(3 \times 3\) Convolution을 추가하여 spatial information을 학습한다.
Representation head designs
Main Body 이후 head는
- Classification: Low resolution을 사용
- Pose Estimation: High resolution에서 regression head만 추가
- Segmenatation: 전체 resoltuion 모두 사용 (low resolution을 upsampling)
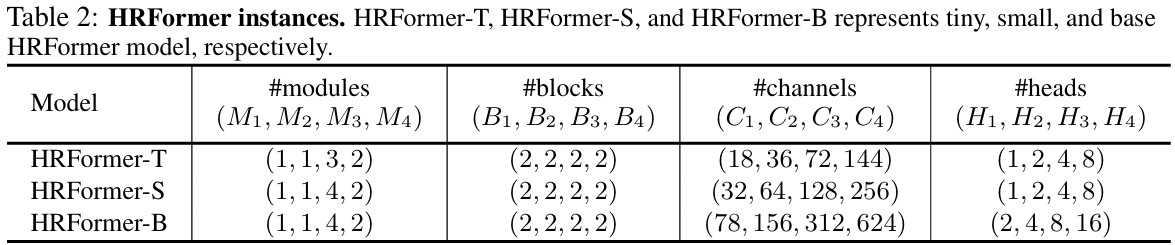
Architecture & Human Pose Estimation
Local window의 사이즈는 모든 해상도에서 \(7 \times 7\)을 사용했고, 자세한 내용은 아래의 표와 같다.