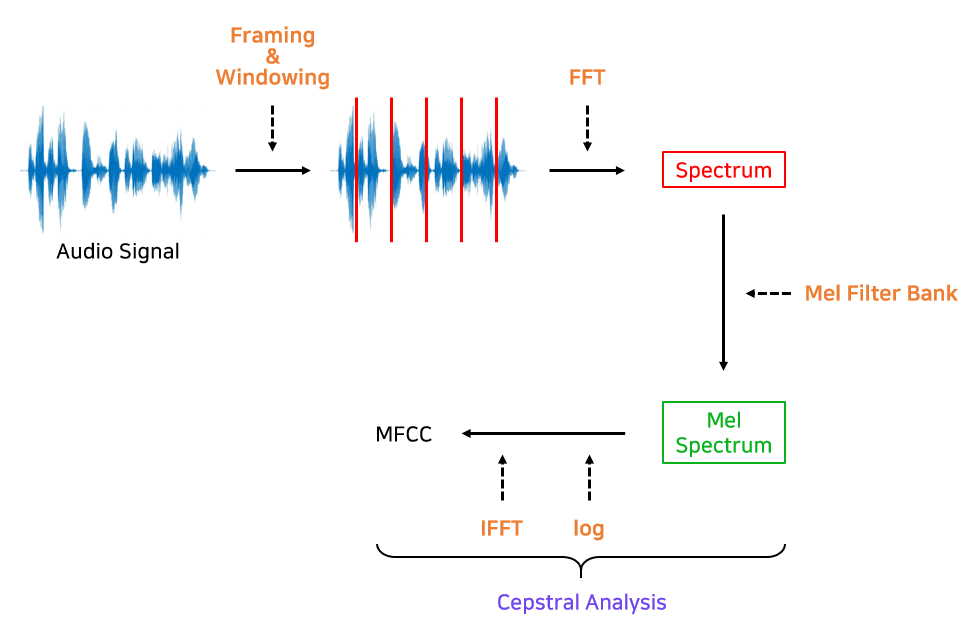
StyleTalk
StyleTalk: One-shot Talking Head Generation with Controllable Speaking Styles
Table of contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Proposed Method
- Objective Function Design
- Experiments
- Conlcusion
- Limitation
- Supplementary
- Code
- Related Work
- Reference
Abstract
사람마다 말하는 스타일과 화법이 다른데, 기존의 one-shot talking head generator 들은 다양한 화법 스타일에 대한 생성이 어려웠음
임의의 reference talking vedeo에서 말하기 스타일을 얻은 다음 reference 스타일과 다른 오디오로 말하기 위한 one-shot portrait
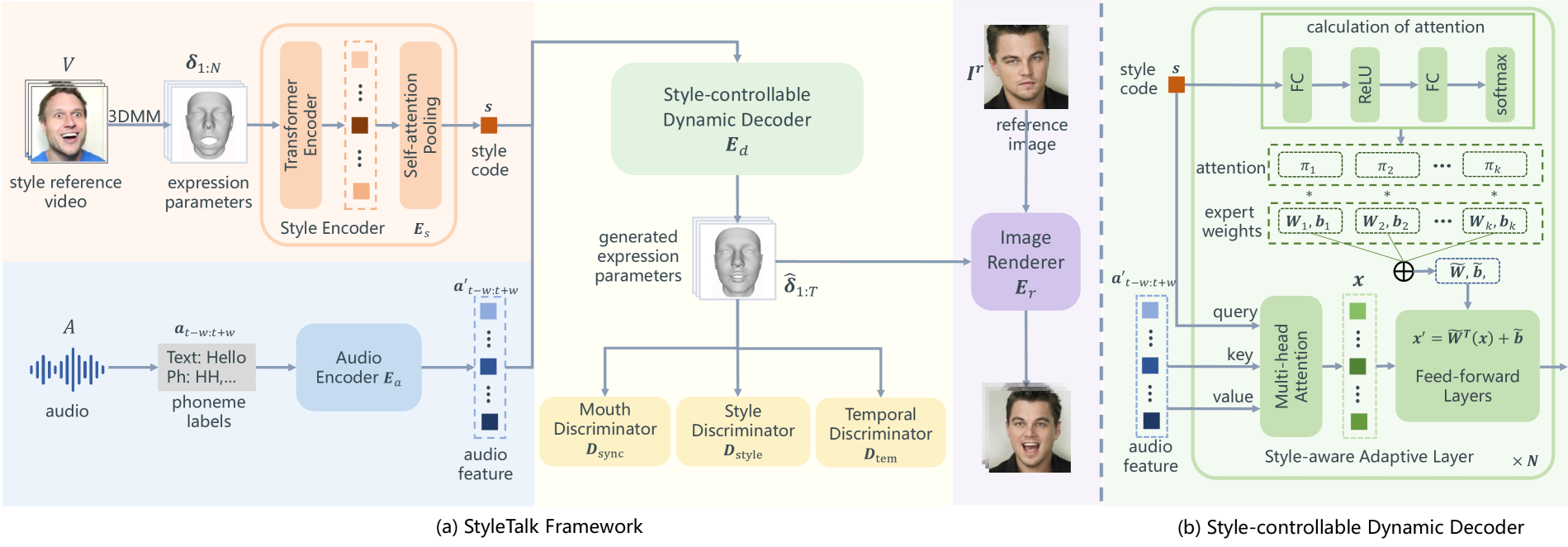
style reference의 얼굴 동작 패턴 추출 후 portrait에 style code로 인코딩 (style encoder)
이후, voice와 style code에서 stylized facial animation을 합성하는 style-controllable decoder (style-aware adaptation 사용)
style 적용에 가중치를 주기 위해 adjust the weight
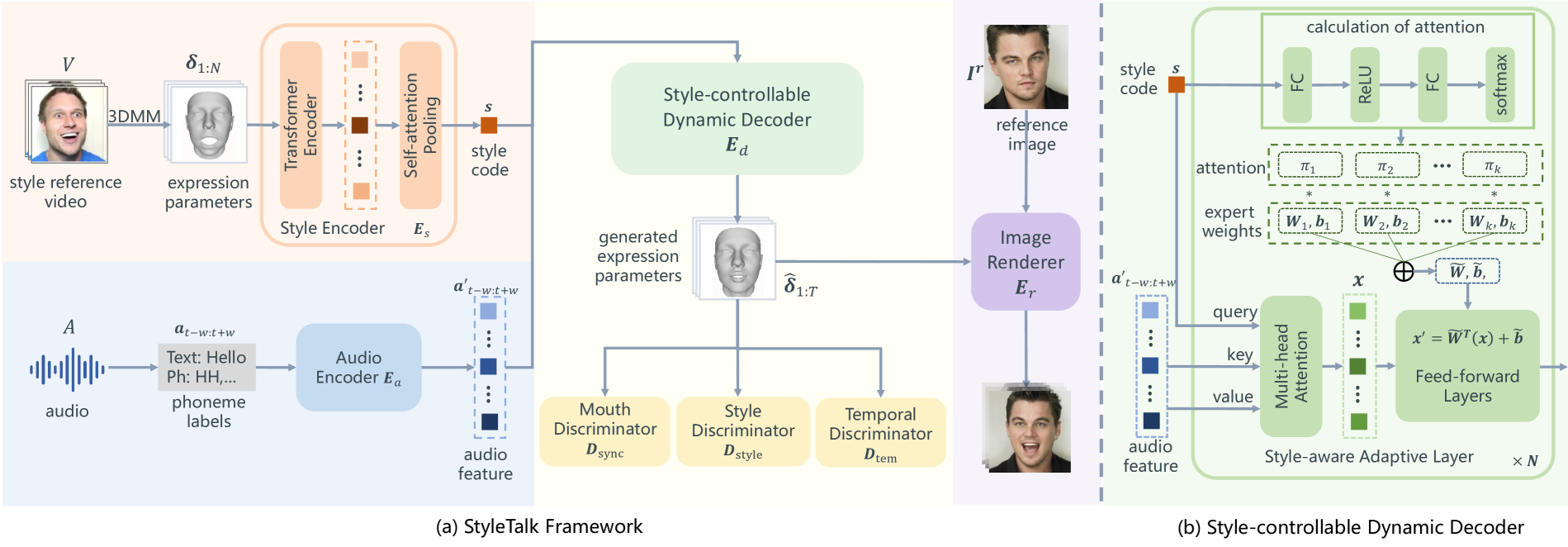
- style video로부터 3DMM parameter 추출 후, style code \(s\)를 얻기 위해 encoder \(E_s\)에 feeding
- Audio Encoder \(E_a\)를 통과하여 audio에 대한 feature 추출
- 두 feature가 Style-controllable Dynamic decoder에 입력, stylized expression parameter를 얻음
- Image renderer \(E_r\)에 stylized expression parameter \(\hat{\delta}\)와 identity reference image \(I_r\)을 feeding하여 output video 생성
오른쪽 이미지 (b)는 style-controllable dynamic decoder의 세부 설명
Introduction
Talking head의 경우, virtual human, 더빙 등에서 활용됨
입술, 머리 포즈, 동영상에서 많은 발전이 있었지만, 다양한 화법에 대한 영상 생성은 하지 못함
\(\rightarrow\) one shot에 대하여 (같은 사람이더라도 상황에 따라서 말할 때 스타일이 달라질 수 있음)
따라서, one shot reference 이미지에 대해서 style reference image와 음성을 기반으로, talking head를 생성할 수 있는 방법 제안
이전 방법들은 단순히 감정 class만 가지고 생성하거나 단일 프레임에 대하여 style을 전달받음
따라서 말하는 스타일을 동작 패턴으로 나타내어 style을 전송할 수 있는 방법 제안
- style 영상과 오디오로부터 인코딩된 feature를 얻음
- style 영상의 3DMM (3D Morphable Model)의 sequence로부터 style latent code \(s\)를 추출하기 위하여 self-attention pooling layer가 있는 transformer 기반 style encoder를 이용
- triplet constraint을 사용하여 unseen style clip에 대해서도 적용할 수 있도록 함
- 학습된 style code \(s\)가 semantically meaningful space에 있음을 확인
- style-controllable dynamic decoder에 input으로 넣어, 3D 얼굴 애니메이션을 얻음
- style code를 통해 조건부 일대일 mapping으로 바꾸었지만, 표정의 변화가 큰 경우에는 여전히 불만족스러운 립싱크 및 시각적 아티팩트를 볼 수 있음
- 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 style-controllable dynamic decoder 제안
- multi-head attention 뒤의 feed-forward layer가 style 제어에 중요함
- 따라서, style code \(s\)를 기반으로 FF의 kernel weight를 adaptively 생성
- \(s\)를 FF에 태워서 attention 계산
- 따라서, one-shot setting의 일대다 mapping에서 일대일 mapping으로 전환
- 더 효과적으로 립싱크를 생성하고 설득력있는 얼굴 생성
- Image renderer를 이용하여 reference와 3D 얼굴 애니메이션을 입력으로 하여 rendering
Contribution:
- 하나의 대상 이미지에서 다양한 스타일의 말하는 비디오를 생성하는 one-shot 제어 가능한 talking head 프레임워크를 제안
- universal style extractor를 제안하여 다양한 unseen clip에 대해 잘 동작하도록 함
- style-controllable dynamic decoder를 이용하여 정확하게 stylize된 얼굴과 입술 생성
Proposed Method
3개의 input을 사용하는 새로운 style-controllable talking face generate framework 제안
- Reference image \(I^r\)
- Audio Clip \(A\): speech content를 제공하는 \(T\) 길이의 오디오
- Style Clip \(V\): style reference talking video \(V = I^s_{1:N}\) (길이 \(N\))
Output은 photo-realistic taking video \(Y(=\hat{I}_{1:T})\)
\(\rightarrow\) reference의 얼굴을 가진, style clip 표정의 비디오
아래의 그림과 같이 4 부분으로 이뤄짐
- Audio encoder \(E_a\): 음소 단위의 label \(a_{1:T}\)로부터 분절된 feature의 sequence \(a'_{1:T}\)를 추출
- Style encoder \(E_s\): 얼굴의 동작 패턴을 compact한 style code \(s\)로 추출
- Style-controllable dynamic decoder \(E_d\): audio feature와 style code \(s\)로부터 stylized 3DMM expression parameter \(\hat{\delta}_{1:T}\) 생성
- Image renderer \(E_r\): reference image와 expression parameter로부터 사실적인 talking face 생성
훈련의 경우 \(\{I^r, a_{t-w,t+w},V\}\)를 input으로 하여 Wang의 방법을 사용함
\(\rightarrow\) \(w\)는 window length이고, 5로 설정됨

Audio Encoder
음소 단위의 label \(a_{1:T}\)로부터 분절된 feature의 sequence \(a'_{1:T}\)를 추출
하지만 오디오는 talking-style에 영향을 미치는 감정이나 강도같은 정보와 무관한 정보를 포함
이런 정보를 없애기 위하여 MFCC 같은 acoustics feature가 아닌 phoneme label을 사용
\(\rightarrow\) ASR로 음성에서 텍스트 추출 후, phindex.json에 mapping
phoneme label \(a_{t-w,t+w}\)는 word embedding을 통하여 바뀌고, transformer encoder로 들어가, audio feature를 얻음 \(a'_{t-w,t+w},\; a'_t\in \mathbb{R}^{256}\)
phoneme은 음성 인식 툴에서 추출됨
Style Encoder
얼굴의 동작 패턴을 compact한 style code \(s\)로 추출
speaking style은 얼굴 표정 패턴이기 때문에 얼굴의 모양, 텍스쳐, 조명과는 무관함
이런 불필요한 정보를 없애기 위해, 3DMM 사용하여 style video clip을 sequantial한 expression parameter \((\delta_{1:T}\in\mathbb{R}^{N\times64})\)로 변환
추가적으로 이미지의 정적인 표현뿐만 아니라, 동작 패턴을 modeling하는 style encoder 설계
Transformer encoder로 구성되어 있고, sequential 3DMM을 input token으로 사용
encoder는 각 token에 대한 style vector \(s'_{1:N}\)를 출력
\(\rightarrow\) 몇 frame을 입력으로 넣어, self-attention으로 집계하여 출력
\(\rightarrow\) 추가적으로, FF에 token level에서 weight를 계산하는 추가적인 attention-based mechanism 사용
\(\rightarrow\) 여기서 각 token은 비디오에서 각 frame이 style에 기여하는 weight 임
\(\rightarrow\) 각 weight를 다 더해서 최종 style code \(s\in\mathbb{R}^{d_s}\)를 얻음
Style-Controllable Dynamic Decoder
Style Decoder 앞서, articulation representation \(a'_{t-w,t+w}\)와 style code \(s\)를 input으로 받아, vanilla transformer decoder를 적용했었음
style code \(s\)를 \(2w+1\)번 반복하여, positional encoding을 추가한 후 style token들을 얻음
\(\rightarrow\) voice의 latent와 같은 차원이어야하기 때문에 반복하고, style code는 query, articulation representation는 key, value로 들어감
Dynamic Style Decoder 하지만 위의 단순한 decoder는 표정의 움직임이 클 때, 입술과 표정에 artifact가 생김
앞선 다른 연구에서 static kernel weight가 다양한 style을 modeling할 수 없다고 가정했음
따라서, style code에 따라 adaptive하게 style-aware adaptive transformer 설계
또한 Wang에서 FF가 transformer decoder에서 중요한 역할을 한다는 것을 밝혔기 때문에 FF에 적용
Style-aware adaptive FF layer를 적용하는데, 8개의 parallel한 layer set weight\((\tilde{W}_k, \tilde{b}_k)\) 사용
\(\rightarrow\) Parallel weight는 각각 다른 talking style을 뚜렷하게 modeling하게 학습될 것이라 기대됨
\(\rightarrow\) 가중치를 적용하기 위해, softmax를 적용한 후, weight sum
따라서, 최종적인 FF layer는
\[y=g(\tilde{W}^T(s)x+\tilde{b}(s)),\;\;g=\mathrm{act\_func}\]Disentanglement of Upper and Lower faces
Upper face (눈, 눈썹)과 lower face (입술)이 다른 움직임 패턴이 있다는 것이 관찰됨
\(\rightarrow\) 별도로 모델링하는 것이 타당하였음
따라서, expression param을 두 그룹으로 나눠, upper face decoder와 lower face decoder, 두 개로 parallel하게 style-controllable dynamic decoders를 구성
\(\rightarrow\) 64개 중, 13개가 mouth에 해당하여 lower, 나머지가 upper
\(\rightarrow\) 13개인 이유는 supp.
최종적으론, concatenated되어 output됨
Objective Function Design
output은 한 frame을 뽑아내기 때문에, sequence에 대한 batch를 학습함
한번에 64 frame을 뽑음
64 frame에 3개의 Discriminator를 적용
- \(D_{tem}\): temporal discriminator
- \(D_{sync}\): vertex-based lip-sync discriminator
- \(D_{style}\): style discriminator
또한 semantically meaningful style space를 얻기 위해, triplet constraint를 사용
Lip-sync Discriminator
입술은 말하는 와중에 많이 움직임. 따라서 sync가 중요함
따라서 \(D_{sync}\) 설계
- audio의 window를 random sampling
- video의 window를 random sampling
- 두 window가 sync, async 된 것에 대해 disc 적용
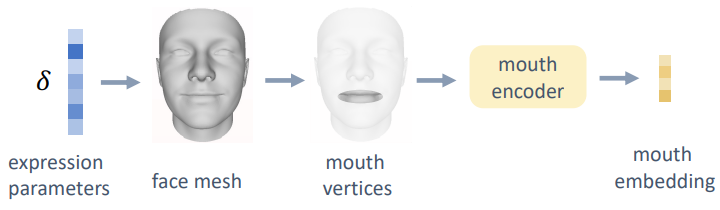
3DMM에서 mouth-related는 얼굴 움직임도 포함하기 때문에, 입술만 추출하기 위해 PCA base로 expression parameter를 face mesh로 바꿔서 입 vertice를 선택
SyncNet에 mesh vertex coordinate와 phoneme를 각각 input으로 넣음
mouth와 phoneme의 window에 대한 emb\((e_m,e_a)\)를 뽑기 위해 pretrained PointNet을 사용
두 emb에 대해 cosine similarity를 적용
\[P_{sync}=\frac{e_m\cdot e_a}{\max(\lVert e_m\rVert_2\cdot\lVert e_a\rVert_2,\epsilon)},\]\[L_{sync}=\frac{1}{L}\sum^L_{i=1}-\log(P^i_{sync})\]
Style Discriminator
전체 style에 대한 loss
sequential 3DMM expression parameters \(\delta_{1:L}\)를 input으로 frozen PatchGAN (CE loss)
\[L_{style}=-\log(P^s_i),\;\; \mathrm{s=speaking\;style}\]
Temporal Discriminator
현실적이지 않은 것을 구별
sequential 3DMM expression parameters \(\delta_{1:L}\)를 input으로 PatchGAN (GAN hinge loss)
Triplet Constraint
유사한 style code는 비슷한 space에 모여있어야 함 (직관적으로)
따라서, style code \(s\)에 triplet contraint
\(c\)의 style을 가진 clip이 있을 때, 다른 style을 가진 clip 두개를 sampling하여 loss 적용
\[L_{trip}=\max\{\lVert s_c-s^p_c\rVert_2-\lVert s_c-s^n_c\rVert_2+\gamma,0\},\;\; \gamma=5 (\mathrm{margin\; parameter})\]
Total Loss
Facial expression의 reconstruction의 경우 L1과 SSIM 적용
\[L_{trip}=\max\{\lVert s_c-s^p_c\rVert_2-\lVert s_c-s^n_c\rVert_2+\gamma,0\},\;\; \gamma=5 (\mathrm{margin\; parameter})\]
최종 loss:
\[L=\lambda_{rec}L_{rec}+\lambda_{trip}L_{trip}+\lambda_{sync}L_{sync}+\lambda_{tem}L_{tem}+\lambda_{style}L_{style},\\ \lambda_{rec}=88,\;\lambda_{trip}=1,\;\lambda_{sync}=1,\;\lambda_{tem}=1,\;\lambda_{style}=1\]
Experiments
Dataset
여러 말하기 스타일이 포함된
- MEAD: 60명의 화자가 8가지 감정의 세 가지 강도 수준으로 말하는 얼굴 코퍼스
- 동일한 강도 수준과 동일한 감정일 때, 동일한 speaking style이라고 가정
- HDTF: In-the-wild audio-visual dataset
- 한 화자의 비디오 클립이 동일한 speaking style이라고 가정
Training set에서 1104개의 speaking style을 얻음
\(\rightarrow\) 256×256로 crop, resized되고 30FPS로 sampling
Implementation Details
Pytorch, Adam
\(E_r\)은 VoxCeleb, MEAD, HDTF를 조합하여 훈련됨
\(D_{sync}, D_{style}\)는 HDTF, MEAD로 12시간 (RTX 3090 GPU 4개, lr: 0.0001)
앞서 훈련된 것들은 fronzen
이후, \(E_a, E_s, E_d, D_{tem}\)은 HDTF, MEAD로 4시간 (RTX 3090 GPU 2개, lr: 0.0001)
Quantitative Evaluation
입술: SyncNet의 confidence score \(\mathrm{Sync_{conf}}\)와 M-LMD(Landmark Distance on the Mouth) 사용
표정: F-LMD(Landmark Distance on the whole face) 사용
비디오 품질: SSIM, CPBD(Cumulative Probability of Blur Detection)
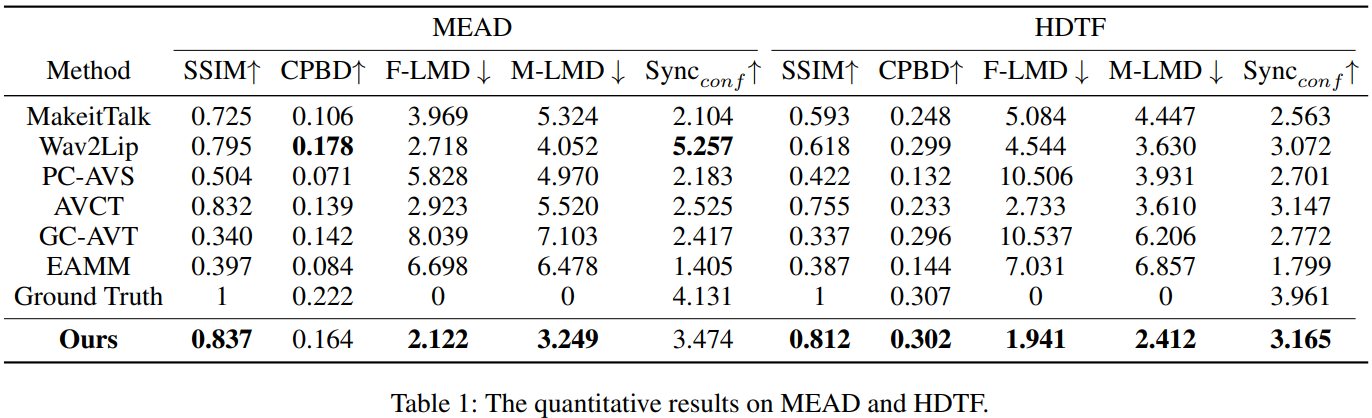
\(\rightarrow\) unseen에 대해 수행
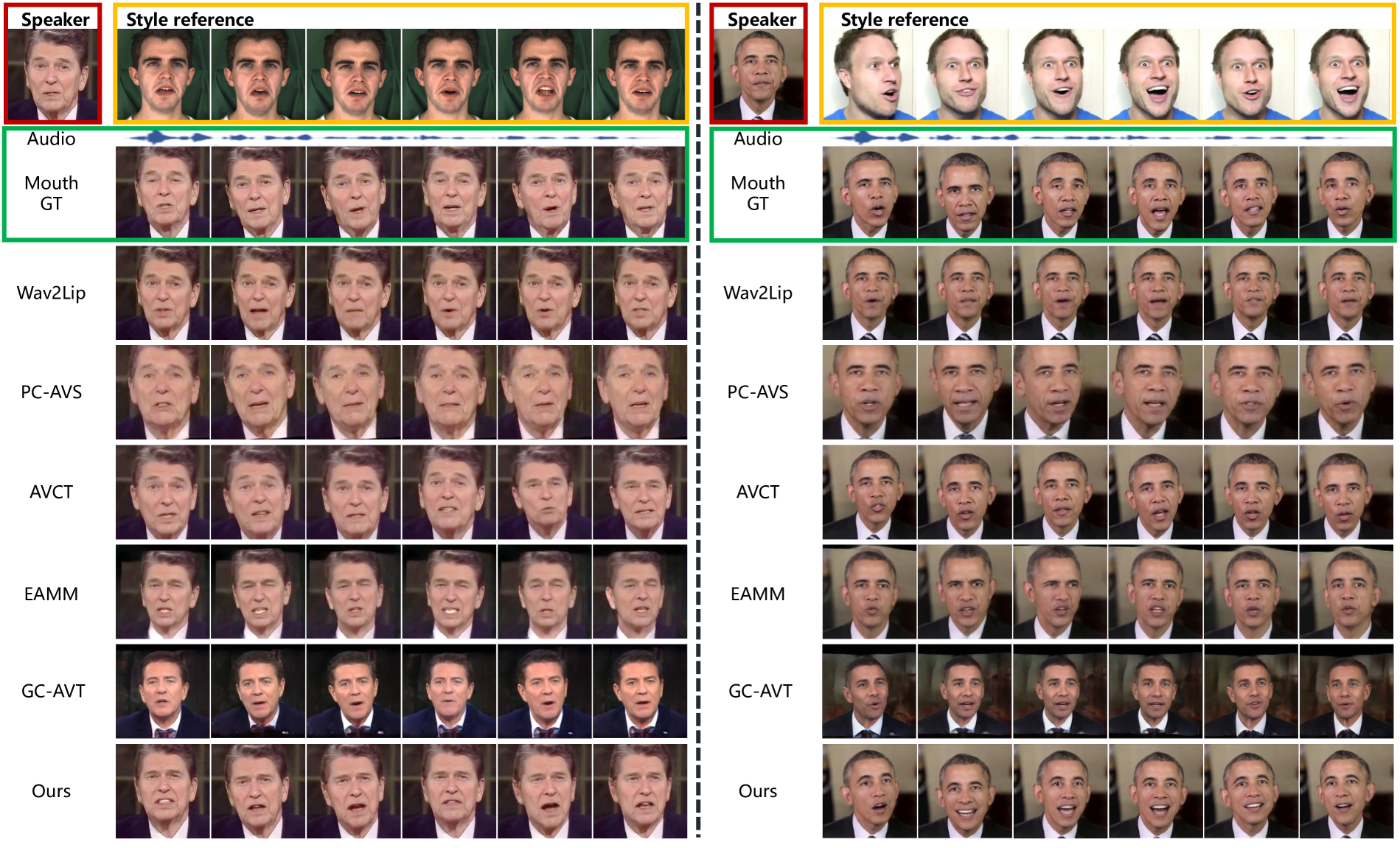
Qualitative Evaluation
EAMM, GC-AVT만 스타일 control 가능하고 꽤나 정확하지만 upper face만 control 가능했음
또한 배경도 부족하고, 스타일의 일치성이 부족함
Wav2Lip, AVCT, PC-AVS, GC-AVT는 입술 생성을 잘하지만, 하나의 화법만 가능
제안된 방법은 정확한 lip-sync, identity 보존 및 좋은 배경 생성을 할 수 있음

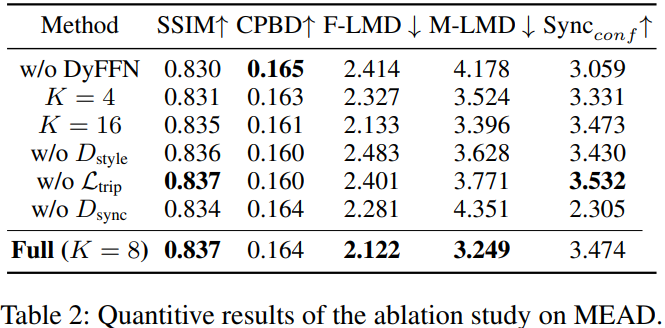
Ablation Study
MEAD dataset에서 6개의 변형
- K=4, 16 \(\rightarrow\) 8일 때가 좋았음
- \(D_{style}\), triplet loss \(\rightarrow\) landmark에 효과적
- \(D_{sync}\) 없애기 \(\rightarrow\) 입술에 효과적

Style Space Inspection
Style Space Visualization
t-SNE를 사용하여 style code \(s\)를 2D에 project
t-SNE는?
불필요한 feature를 없애, vector간 관계성 파악
높은 차원의 데이터를 2차원 또는 3차원으로 축소시켜 시각화
높은 차원 공간에서 비슷한 데이터 구조는 낮은 차원 공간에서 가깝게 대응
- 모든 데이터 포인트 쌍에 대하여 유사도 측정
- low-dim에 무작위 배치하여 유사도 측정
- 2의 유사도가 1과 비슷해지도록 projection 갱신
- 수렴할 때까지 3 반복
즉, KL divergence를 최소화하는 것 (비선형적)
PCA는 공분산에서 eigen vector 계산, 중요한 principal component를 뽑음
\(\rightarrow\) speaker 4명에서 추출
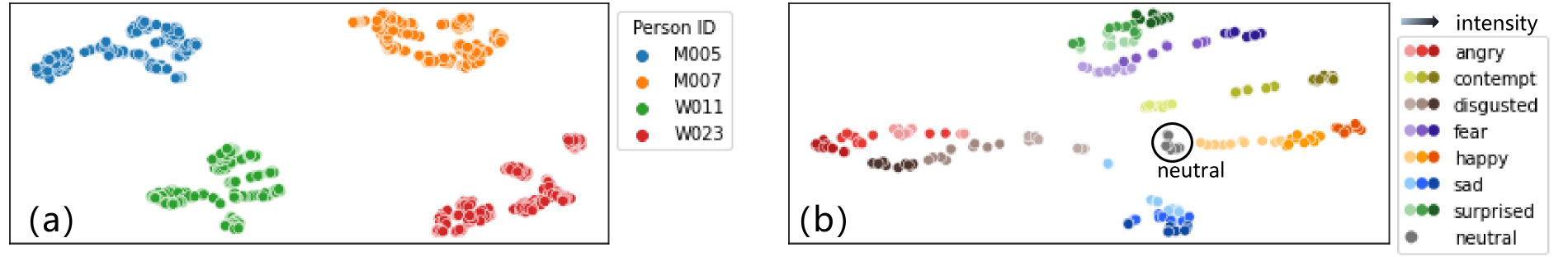
- (a) speaker 내부의 화법이 같은 감정의 다른 speaker보다 가깝다는 것을 의미
- (b) 같은 감정이 잘 clustering됨
- 추가적으로 유사한 감정이 비슷하게 cluster되기도 함 (angry, disgusted)
- 따라서, semantically learn 했다고 볼 수 있음
Style Manipulation
위의 semantically meaningful style code 덕분에 manipulate 가능

- Interpolate in Style Code \(s\)
Conlcusion
- 다양한 style을 가진 one-shot 오디오 기반 talking-head를 생성 framework인 StyleTalk 제안
- Style ref video에서 speaking style 추출 후 대상에 주입
- 시공간적으로 style을 capture
- 정확한 lip-sync와 더 나은 identity 보존 성능
- Condition speaking style과 같은 사실적인 talking-head video 생성
Limitation
- 극단적인 head 방향이나 측면 refer가 있는 style video에서 합리적인 speaking style을 얻지 못함
- 리듬 같은 조음과 무관한 정보를 완전히 제거했기 때문에 output video의 표정의 리듬이 audio와 일치하지 않을 가능성이 있음
- 향후 작업에서는 이러한 정보를 오디오에서 분리하고 이 정보를 프레임 작업에 주입 예정
Supplementary
MFCC
MFCC란?
Mel Spectrum(멜 스펙트럼)에서 Cepstral(켑스트럴) 분석을 통해 추출된 값
소리의 고유한 특징을 나타내는 수치
화자 분류, 음악 장르 분류 등에 쓰일 수 있음MFCC의 추출 과정
- 오디오 신호를 프레임별(보통 20ms - 40ms)로 나누어 FFT를 적용해 Spectrum을 구함
- Spectrum에 Mel Filter Bank를 적용해 Mel Spectrum을 구함
- Mel Spectrum에 Cepstral 분석을 적용해 MFCC를 구함
스펙트럼의 개념으로는 다음이 있음
Spectrum (스펙트럼)
Time domain (시간 x 축, 신호의 진폭 y 축)에서 FFT를 이용하여 frequency domain으로 변환
\[DFT: X_k=\sum^{N-1}_{n=0}x_ne^{-\frac{2\pi i}{N}kn},\;\;\;\; k=0,\cdots,N-1\\ IDFT: x_n=\frac{1}{N}\sum^{N-1}_{k=0}X_ke^{\frac{2\pi i}{N}kn},\;\;\;\; n=0,\cdots,N-1\]
DFT는 discrete signal에 대해 내적 sum을 해가는 것Cepstrum (켑스트럼)
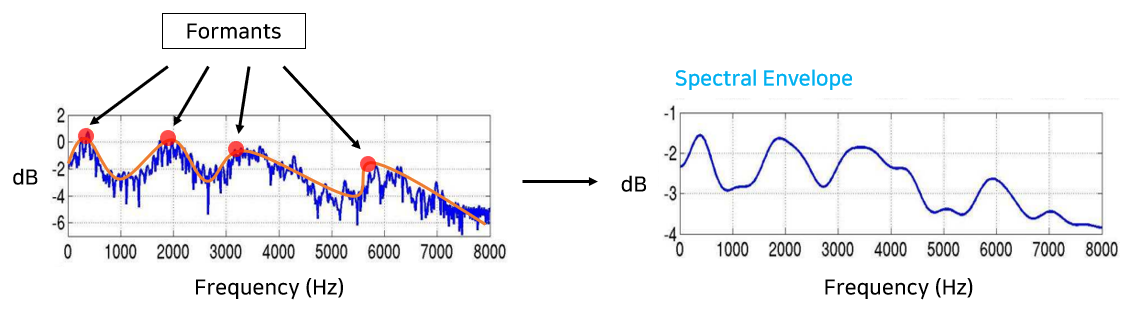
Spectrum에서 정보를 추출할 때 사용하는 방법
음성이나 악기는 일반적으로 화음(배음)을 가지고 있음
배음 구조의 차이가 음색의 차이를 만듬
따라서, Spectrum에서 배음 구조를 유추해낼 수 있다면 소리의 고유 특징을 찾아낼 수 있음Cepstral Analysis
주파수에서 peak점들을 포먼트(Formants)라고 함
\(\rightarrow\) 배음(harmonics)과 만나 소리를 풍성하게 혹은 선명하게 만드는 필터 역할을 함
포먼트들을 연결한 곡선(Spectral Envelope)과 Spectrum을 분리해내면 됨Mel Spectrum (멜 스펙트럼)
사람의 청각기관은 저주파수에 더 민감함 따라서 실제 사람이 인식하는 주파수의 관계를 표현하여 표현한 것이 Mel Scale
Mel Spectrum은 Mel Scale에 기반한 Filter Bank를 Spectrum에 적용하여 도출해낸 것
3DMM
3DMM에서 face shape \(S\)는 affine model을 통하여
\[S=S(\delta,\phi)=\bar{S}+B_{exp}\delta+B_{id}\phi\]\(\bar{S}\)는 평균 얼굴 모양, \(B_{id},B_{exp}\)는 PCA 기반 identity, expression
\(\delta\in\mathbb{R}^{64},\phi\in\mathbb{R}^{80}\)는 각각, 특정 3D face에 대한 coefficient vectors
3DMM
3D Morphable Model
- face의 특징을 PCA에서 eigenvalue를 통해, 평균적인 것부터 얻듯이 3D shape에 weight sum을 하듯이 특징적인 shape를 얻음
- shape는 특징점 vortex의 3차원의 xyz 값으로 나타내어질 수 있음
- texture의 경우 위의 vortex 위치에서의 rgb color로 나타날 수 있음
논문에선, 257 차원의 coefficient 중, 80~144를 expression으로 가진 3DMM을 사용
형태 모델 (Shape Model):
얼굴의 기하학적 모양을 설명
얼굴의 주요 특징을 표현하는 데 사용되고, 주성분 분석(PCA)을 활용질감 모델 (Texture Model):
얼굴의 피부 표면의 질감을 설명
얼굴의 색상, 주근깨, 주름 등을 포함
주로 텍스처 맵(texture map) 또는 텍스처 공간(texture space) 관련 정보를 사용하여 표현조명 모델 (Lighting Model):
조명 조건에 따른 얼굴의 외관을 모델링
얼굴에 빛이 어떻게 반사되는지를 설명하고, 이를 통해 얼굴의 입체감을 부여합니다.표정 모델 (Expression Model):
얼굴 표정과 관련된 정보를 포함
얼굴의 다양한 표정(행복, 화남, 슬픔 등)을 표현하는 데 사용
Input to Lip Sync Discriminator
위에서 identity는 제외하여 적용한, face mesh에서 입 영역의 정점 좌표를 선택
\[M=\bar{S}+B_{exp}\delta\]이후, PointNet을 이용하여, mouth에서 embedding
Implementation Details
Audio Encoder
phoneme은 128로 convert 후 256으로 projection (Linear layer)
sequence=11
Style Encoder
64~256 (N) frame의 비디오를 얻어, linear로 256 dim으로 변환
Audio encoder와 같은 형식을 input으로 하여 style code \(s\in\mathbb{R}^{256}\)추출
Code
Overview
3DMM과 phenom은 다른 model로부터 이미 준비되어야 함
각각, encoder에 들어가서 output을 얻은 후, 둘을 decoder에 넣음
decoder의 output인 expression param은 head pose와 concate되어, renderer에 같이 들어감
expression은 frame window 만큼 stack되고, stack된 elem들은 split_size만큼 묶여 renderer에 들어감
\(\rightarrow\) split_size를 최대 frame window라고 생각해도 될듯 (즉, (frame window, …)로 input이 구성)
renderer에서는 src_img와 위의 expression이 같이 들어가서 image 생성
Related Work
Audio-Driven Talking Head Generation
오디오 기반 talking head 방법은 person-specific과 person-agnostic method로 나뉨
Person-specific은 훈련된 speaker에 대해서만 작동함
일반적으로 3D 얼굴 애니메이션을 먼저 제작한 다음 realistic talking video를 합성
몇몇 방법들은 high-fidelity talking head를 위해 Nerf를 사용
Person-agnostic은 one-shot에서 talking-head video 생성을 목표로 함
초기에는 speech에 맞는 lip 생성에 초점을 맞춤
이후 얼굴 표정과 머리 포즈를 고려한 방법이 나옴
하지만 표현력이 풍부한 stylized talking-head video를 생성할 수 없었음
Stylized Talking Head Generation
talking-head에 얼굴 표정을 고려한 방법들
Ji(2021)는 audio에서 content와 감정을 extract하여 예측한 landmark로 생성되도록 guide
\(\rightarrow\) 하지만 오디오만 고려하기 때문에 정확성이 모호하고 적용 가능성을 제한
Wang(2020)과 Sinha(2022)는 emotion label을 input으로 사용
Ji(2022)와 Liang(2022)은 frame 별로 화자의 표정을 input으로 전달
즉, 이전 방법들은 얼굴 표정의 temporal, spatial feature를 고려하지 못함